Users do not trust LLMs. The data tells the story.
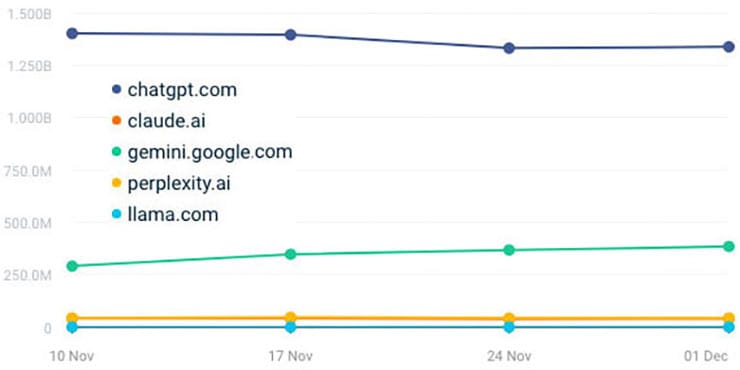
Over the past 21 days, traffic across major LLM platforms has moved in one unmistakable direction:
- ChatGPT fell from 220.3 million daily visits to 212.6 million.
- Claude declined.
- Perplexity slipped.
Three of the four leading platforms are drifting downward at the exact same time — a signal, not a coincidence. These are not seasonal ripples or random fluctuations. They are the early signs of an adoption stall.
Only one platform moved in the opposite direction: Google Gemini, rising from 45.28 million daily visits to 58.69 million — nearly a 30 percent increase.
Why?
First, Sam Altman has publicly said Gemini has surpassed ChatGPT.
Second, Google begins with the largest ready-made audience in the world. So Google can push users to try Gemini 3, but it is too soon to tell whether users will adopt Gemini 3.
But based on the failed rollout of Gemini 1.0 and 1.5 – which failed due to hallucinations – Gemini 3 faces the same risk because its hallucination rate is 88%.
And that is where the real story begins. Gemini’s rise does not change the broader truth: across ChatGPT, Claude and Perplexity, user engagement is flat or declining:
- Capability isn’t the problem.
- Compute isn’t the problem.
Users are stepping back because LLMs behave inconsistently:
- They forget context.
- They contradict themselves.
- They hallucinate confidently.
- They lose track of constraints and prior corrections.
In other words: users do not trust LLMs.
Neither does Salesforce
Recent reporting shows that one of the world’s largest enterprise software firms, Salesforce, has publicly acknowledged declining executive trust in large language models and is scaling back reliance on them after reliability issues, including widespread customer problems and workforce impacts.
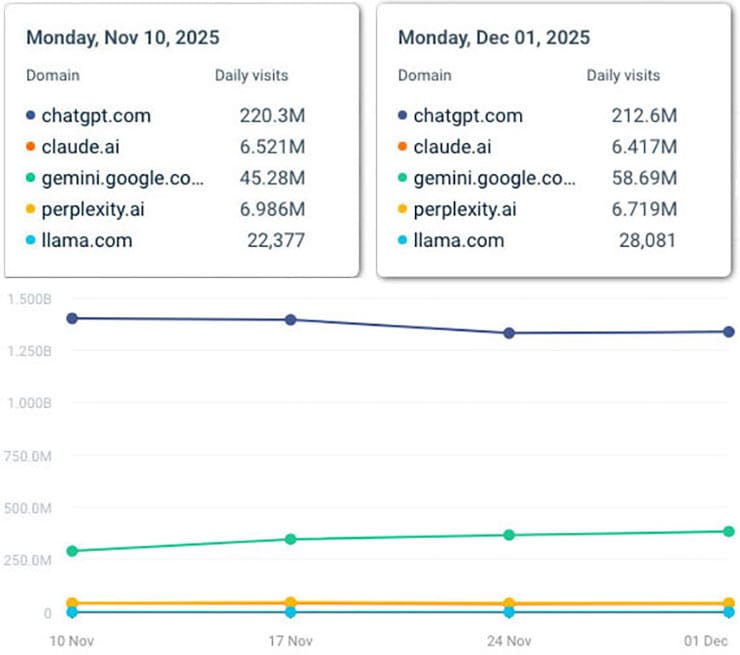
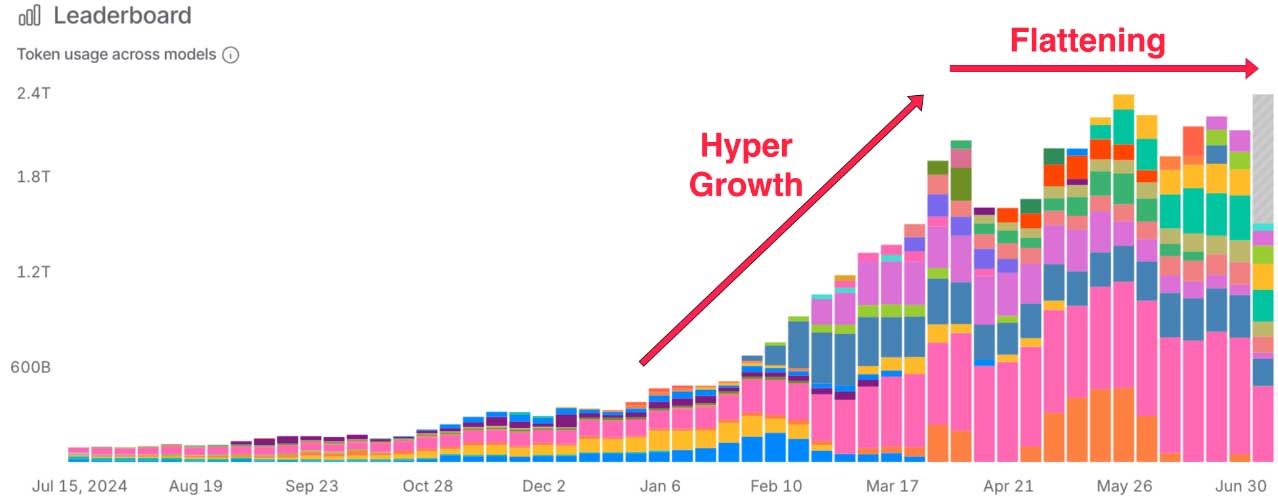
The chart, above, shows a flat trend for three out of four LLMs based on traffic in November. This tracks with flat trend we reported on here, with data from August through October. You can see that the flat trend began last spring in the chart, below, based on token usage across models.
Adoption hinges on trust, and trust hinges on memory. Bigger models don’t fix continuity. More compute doesn’t fix grounding. Scale doesn’t fix inconsistency.
Until LLMs can remember what they’ve learned, maintain constraints over time and behave reliably across sessions, adoption will remain stalled — no matter how fast they think.
If AI wants to grow, it must remember to stop forgetting.
